- MAIN PAGE
- – elvtr magazine – MANAGING A TEAM: 9 “DON’TS” YOU NEED TO REMEMBER
MANAGING A TEAM: 9 “DON’TS” YOU NEED TO REMEMBER

Managing a team can be safely called not just a science, but a real art. Good managers safeguard company order that keeps their employees happy. Those workers are glad to come to work every day, and they are ready to continue working for a long time in this company.
Naturally, such dedication cannot arise in an empty place. It is always the result of systematic work on the creation and development of a team. For this to happen, teams require good leaders with vision and practised skills.
But at this point reality bites. CareerBuilder`s survey showed, that 26% of managers weren't ready to become team leaders when they started supervising others. When managers were asked about the biggest challenge in their work, they gave the following answers:
- Acting toward the issues between coworkers on the team – 25%
- Motivating their employees – 22%
- Performance reviews – 15%
- Searching for resources to reinforce the team – 15%
- Creating career paths for the team – 12%
Another poll demonstrated that inconsiderate and dull leaders are among the top causes for workers to quit their jobs.
So how can one in a manager’s position avoid such a misfortune path? Let`s overview the most common mistakes a team leader can make.
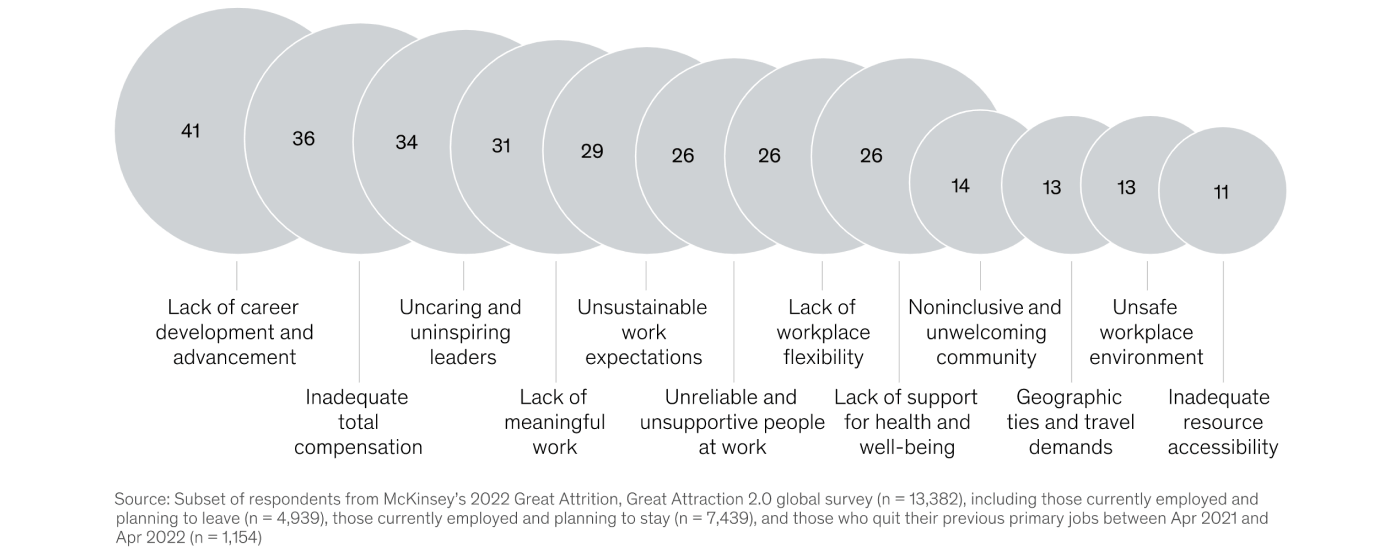
Top reasons for quitting previous job, Apr 2021–Apr2022, %.
Source: mckinsey.com
#1. Not Keeping Promises
In an attempt to motivate people, some managers make false promises, which is absolutely unacceptable for leaders. This not only demotivates the employee but can also have a negative impact on the company as a whole.
With each commitment leader upholds to their employees, they become more trustworthy and dependable in the eyes of the team. But if a leader does not keep their promises, how can he expect anyone around him to do so?
Stephen Gregg, founder and CEO of Apex says, that people do not follow leaders who don`t commit. Commitment can be executed in a different range of matters and include:
- preferable work hours
- how you improve your skills and abilities
- what you do for your employees at a personal sacrifice, etc
#2. Ignoring Ineffective Employees
Careless performers in a team can de-motivate good and excellent performers. They will influence the performance of other teammates as well as the team's overall success.
The longer a manager waits to address this poor performance problem, the higher the risk of decreasing the team's productivity and losing their best employees.
You need to develop your ability to explore the tough truth about people`s productivity and open the door to greater performance.
#3. Avoiding Changes
Without change, organizations like all organisms, perish and eventually die. Leaders who fail to drive change pose a serious threat to their organizations. They fear the unknown or the discomfort that comes with moving on to something new. And such an attitude may leave your company behind the others, who embrace changes and grow.
For example, Netflix`s case can show us the importance of changes. In the beginning, the company worked with movies on DVD. They offered monthly subscriptions to get movies delivered to the customer`s door by postal services. But in 2007 began the streaming video era, and subscribers no longer needed to wait for DVDs to come through the mail.
Netflix chose to address the needs of the consumers that wanted to watch content online and implemented changes successfully. At that stage, their long-term survival was dependent on how they managed to adapt to a digital future.
This change helped Netflix survive a drop in subscription numbers and stock figures. Netflix subscribers were:
- 23 million in 2011
- more than 137 million in 2018
So we can see that their plan worked. And the business realized that DVDs were on their way out, so the company needed to shift its wheels.
Understand the benefits that change and innovation will bring, and stop resisting. Your job is to be a "safe base" that provides a sense of security, as well as encouragement and energy to explore new things. In other words, you must care enough to encourage growth, not support stagnation.
Recommended courses
#4. Rejecting The Thoughts And Ideas Of Others
Some managers are frightened of employee enthusiasm. They prefer to strictly follow the plan and not allow experiments in the company. Constant termination of the initiative and encouragement of mediocrity is perhaps the main managerial mistake. A miscalculation, which leads to the loss of valuable personnel. This is a signal that the manager is petrified of change, which means development.
When a manager dismisses the ideas of others, the message is sent that he or she is smarter than the rest of the team. Over time, people will stop sharing their ideas and innovations and will keep everything to themselves.
According to a poll conducted by Interact/Harris, 63% of workers did not feel heard at work. These findings highlight that employees need to feel more valued and listened to. Employees are more likely to be accountable for their work if they have a voice in what they’re doing.
In 2008, the Google corporation started Project Oxygen study to figure out the most important qualities of an ideal manager. This was one of the most valuable conclusions: “The best managers give people freedom: they allow them to implement and explore their ideas. To do this, they create psychological safety for the team.”
It is important for you to understand that the initiative usually comes from the employees most involved in the company's work. Give people room for creativity, but do not forget about responsibility.
#5. Micromanagement
It is a destructive leadership style that does not provide opportunities for team members to grow. It places an unnecessary burden on team leaders who must monitor team members' every move.
Henry Stewart, business author and CEO of Happy said that in his eyes, micro-management is the number one frustration employees experience. And his words are in line with the Elmo group research. Their Culture Economy Report revealed, that 21% of respondents regard micromanagement as a reason for distrust.
Disadvantages of micromanagement:
- The behaviour of a micromanager is often manifested due to a lack of confidence in the abilities of team members. And the team can`t prove themselves because they never have the opportunity to do so.
- As the project manager tries to control every action, the team members lose their decision-making autonomy.
- Micromanagers often only harm themselves. They spend too much time on work that does not require their participation instead of dealing with strategic challenges.
Perhaps you really have a good understanding of the issue and really know how to do it better. But this fact should never affect the internal comfort of employees. You need to give your employees room for action and the right to make mistakes.
Janna Cachola, author of "Short Journey" offers to get rid of the hyper-control style. She suggests a new term – microencouragement. It's the leaders` role to innovate in how we lead our people.
#6. Non-efficient Delegating
A manager's primary job is to get work done through the efforts of other people, which means they need to delegate. Many managers, especially new ones, struggle with this responsibility.
The reluctance to delegate is often driven by fear of:
- losing control
- losing the "expert" reputation
- having to face the unknown
Remember that delegation is much more than handing over a task or a decision. Google corporation makes the following recommendations for team leaders:
- Make sure that employees know what results need to be achieved and how to do it. And also – by what indicators they will be evaluated.
- Connect the dots. Explain to the employee how their job and new area of responsibility will affect the company and what value it will bring.
Another side of the same mistake is to delegate everything to just one (or few) people. It is wrong to believe that talented specialists can and are obliged to take on additional tasks without negative consequences. And the more talented the employee, the more they can be loaded by default and without an increase in wages.
Вut an employee is forced to work overtime they become over-exhausted. They start thinking about transferring to another company where they can show their talents without pressure from above.
Studies show, that 21% of employees feel overwhelmed with their workload “most of the time.” A Gallup survey revealed that an “unmanageable workload” is the 2nd-leading cause that employees state for being burnt out.
What to do:
- Realise that sooner or later you (or your overloaded employee) will need help. You do not have enough resources to do everything yourself.
- Understand that a manager's effectiveness is related to the skills of organising the team's work.
- Start delegating tasks to employees depending on their level of knowledge and competence.
#7. Not Embracing Your Own Mistakes
A leader must be aware of their shortcomings and mistakes. Dale Carnegie Training polled 3,100 workers in 13 countries. From junior employees to CEOs.
This study found that "admitting when they are wrong" was one of the most important leadership behaviours for employees. And at the same time, it was rarely performed by supervisors.
84% of employees want leaders who have the humility to admit when they are wrong. But only 51% of supervisors do this regularly.
#8. Ignoring Conflicts Inside The Team
It is impossible to avoid uncomfortable conversations or contradictions in the team all the time. No organization is immune to misfortune, wrong decisions, or employees' personal problems. Life can`t always be sunshine and butterflies, even if you pretend very hard.
Many leaders try to ignore negative emotions in the place of work, but that attitude can be costly. Unresolved conflicts block cooperation and agreement around common goals. Tension, negative emotions, and polarization are building up in time.
But if you decide to address the conflict in the beginning, you might win from the situation. Negative emotions not only mark obstacles but also unleash opportunities. Moreover, contradictions are necessary as they might:
- show a real picture of the situation in the company
- provide feedback
- broaden the projects` perspectives
- stimulate thinking and discussion to a new horizon
Employees should challenge each other's ideas and decisions to bring something new to the company's development. However, these conversations and arguments should not be hostile, but professional. They need to aim for mutual assistance and the generation of new ideas.
#9. Ignoring The Necessity Of Employees` Education
It is a common opinion to think that employees should care about their education themselves. And when a person is hired for a job, they are already equipped with the necessary knowledge and skills. But this picture is far from reality.
Studies show that 51% of newly joined employees in the engineering field don’t have the required skills. So employers need to train them for better performance.
Degreed and Harvard Business Publishing Corporate Learning conducted a survey that showed dreary, but not surprising numbers:
- only 40% of workers admitted that their supervisor helps them to figure out the skills they need to advance in their careers
- 22% of workers shared that their supervisors do not stimulate or enable learning at all
- just 17% said their supervisors help design a plan or set goals for developing new skills
People want to expand their skills and competencies while doing their jobs. A good supervisor needs to understand that learning is an integral part of achieving results.
As a head of the team, you should identify areas where you can help your employees learn new skills. By making learning a priority, you become a great leader who can spot and develop talent in people who may not be aware of it themselves.
Reading recommendations for leaders:
- The Power of Flexing. How to Use Small Daily Experiments to Create Big Life-Changing Growth. Susan J. Ashford
- The Effective Executive. The Definitive Guide to Getting the Right Things Done. Peter F. Drucker
- Management. Tasks, Responsibilities, Practices. Peter F. Drucker
- Managing In Turbulent Times. Peter F. Drucker
- The E-Myth Manager. Why Most Managers Don't Work and What to Do About It. Michael E. Gerber
- The Leadership Challenge, James M. Kouzes and Barry Z. Posner
- Change Insight: Change as an Ongoing Capability to Fuel Digital Transformation. Pearl Zhu
*ELVTR is disrupting education by putting proven industry leaders in a virtual classroom with eager rising stars. ELVTR courses offer 100% instructor driven content designed to give you practical knowledge within a convenient time frame. Choose the right course for you!